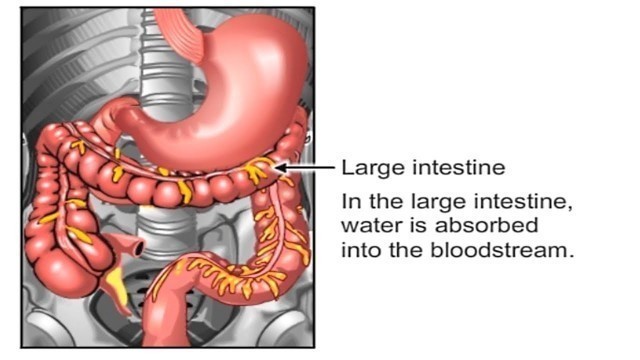

'Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed. The strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle in the esophagus carry the food to the stomach, where it is churned into a liquid mixture called chyme. Next, peristalsis continues in the small intestine where it mixes and shifts the chyme back and forth, allowing nutrients to be absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine walls. Peristalsis concludes in the large intestine where water from the undigested food material is absorbed into the bloodstream. Finally, the remaining waste products are excreted from the body through the rectum and anus. The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that processes food. In order to use the food we eat, our body has to break the food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to excrete waste. Most of the digestive organs (like the stomach and intestines) are tube-like and contain the food as it makes its way through the body. The digestive system is essentially a long, twisting tube that runs from the mouth to the anus, plus a few other organs (like the liver and pancreas) that produce or store digestive chemicals. The Digestive Process: The start of the process - the mouth: The digestive process begins in the mouth. Food is partly broken down by the process of chewing and by the chemical action of salivary enzymes (these enzymes are produced by the salivary glands and break down starches into smaller molecules). On the way to the stomach: the esophagus - After being chewed and swallowed, the food enters the esophagus. The esophagus is a long tube that runs from the mouth to the stomach. It uses rhythmic, wave-like muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throat into the stomach. This muscle movement gives us the ability to eat or drink even when we\'re upside-down. In the stomach - The stomach is a large, sack-like organ that churns the food and bathes it in a very strong acid (gastric acid). Food in the stomach that is partly digested and mixed with stomach acids is called chyme. In the small intestine - After being in the stomach, food enters the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. It then enters the jejunum and then the ileum (the final part of the small intestine). In the small intestine, bile (produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder), pancreatic enzymes, and other digestive enzymes produced by the inner wall of the small intestine help in the breakdown of food. In the large intestine - After passing through the small intestine, food passes into the large intestine. In the large intestine, some of the water and electrolytes (chemicals like sodium) are removed from the food. Many microbes (bacteria like Bacteroides, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella) in the large intestine help in the digestion process. The first part of the large intestine is called the cecum (the appendix is connected to the cecum). Food then travels upward in the ascending colon. The food travels across the abdomen in the transverse colon, goes back down the other side of the body in the descending colon, and then through the sigmoid colon. The end of the process - Solid waste is then stored in the rectum until it is excreted via the anus. Peristalsis is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagates in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. In much of a digestive tract such as the human gastrointestinal tract, smooth muscle tissue contracts in sequence to produce a peristaltic wave, which propels a ball of food (called a bolus while in the esophagus and upper gastrointestinal tract and chyme in the stomach) along the tract. Peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed material to keep it from moving backward, then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. Earthworms use a similar mechanism to drive their locomotion, and some modern machinery imitates this design. What is the digestive system? The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract—also called the digestive tract—and the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus. The hollow organs that make up the GI tract are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine—which includes the rectum—and anus. Food enters the mouth and passes to the anus through the hollow organs of the GI tract. The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are the solid organs of the digestive system. The digestive system helps the body digest food. Bacteria in the GI tract, also called gut flora or microbiome, help with digestion.'
Tags: body , video , animation , biology , stomach , digestion , human body , explained , digestive enzymes , Anatomy , esophagus , digestive system , physiology , large intestine , anus , digestive tract , small intestine , rectum , peristalsis , chyme , how food is digested , swallowing mechanism , gastrointestinal system , how food digests , Peristaltic Movement , peristalsis animation , peristalsis movement video , intestinal peristalsis , digestive system parts and functions , gis , peristaltic waves , motility
See also:
















!['RAW shopping to RAW Dinner Day for Oliang&nomyen [ASMR] MUKBANG 犬が生の肉を食べる[咀嚼音] Dog VLOG'](https://cdn-img01.foodbl0g.com/images/40-m/783/783928_m.jpg)
comments